If the rented space was used to manufacture goods, the rent would be part of the cost of the products produced. Generally, expenses are debited to a specific expense account and the normal balance of an expense account is a debit balance. When an account has a balance that is opposite the expected normal balance of that account, the account is said to have an abnormal balance. For example, if an asset account which is expected to have a debit balance, shows a credit balance, then this is considered to be an abnormal balance. The mean of the \(z\)-scores is zero and the standard deviation is one.
Normal Debit and Credit Balances for the Accounts
Even if a phenomenon may be represented as the combination of many factors, if one of those factors outweighs the others, then the distribution will often not be normal. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. Sales are reported in distributions normal balance the accounting period in which title to the merchandise was transferred from the seller to the buyer. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. This means that 70% of the test scores fall at or below 65.5 and 30% fall at or above.
What is a Normal Account Balance?
- The curve approaches the \(x\)-axis, but technically never touches it.
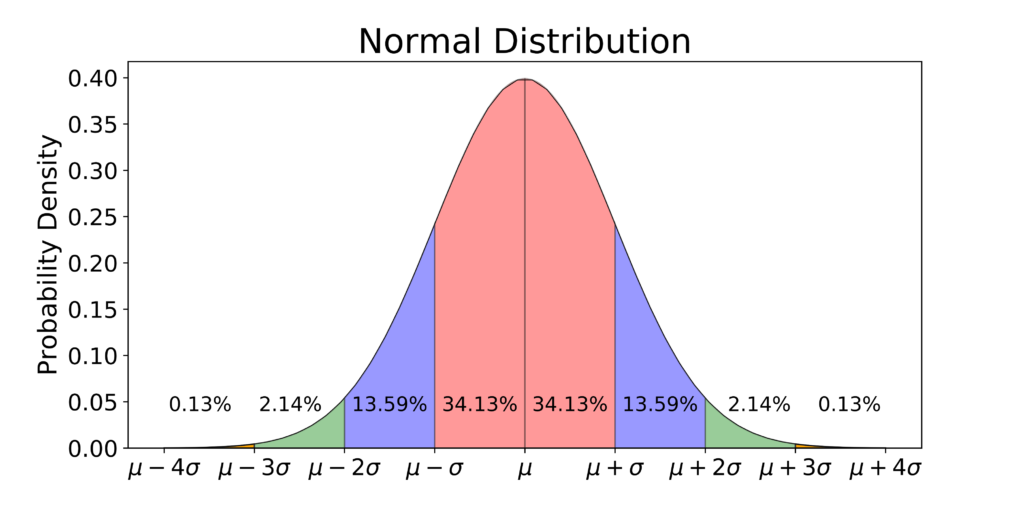
- A Z-table tells you the area underneath a normal distribution curve, to the left of the z-score.
- If the customer purchased on credit, a sales allowance will involve a debit to Sales Allowances and a credit to Accounts Receivable.
The value of \(z\) represents the number of standard deviations the given value of \(x\) is above or below the mean and is usually rounded to 2 decimal places. Because so many real data sets closely approximate a normal distribution, we can use the idealized normal curve to learn a great deal about such data. With a practical data collection, the distribution will never be exactly symmetric, so just like situations involving probability, a true normal distribution only results from an infinite collection of data. Consider this alternative scenario where the red distribution signifies the runs in 2009, while the black one represents the runs in 2010. Notably, the mean, standard deviation, and skewness of both distributions are identical.
Standard Normal Variate : (z-score)
We’ll see how it helps us guess things and why it’s used in many different areas, from science to everyday life. Whether you love or hate numbers, we’ll uncover how this ‘bell curve’ helps us understand the world around us better. A new product was released and a survey asked customers to give the product a score between 1 and 100. At first, when the number of subjects \((n)\) was still relatively low, the company couldn’t pull much information from the surveys.
In contrast, in a skewed distribution, the mean, median, and mode are not equal, and the distribution tends to have a longer tail on one side than the other. There is no closed form expression for the cumulative density function. A \(z\)-score table usually takes the following form, where the column determines the hundredths digit of the \(z\)-score and the row determines the tenths and units digit. An allowance granted to a customer who had purchased merchandise with a pricing error or other problem not involving the return of goods. If the customer purchased on credit, a sales allowance will involve a debit to Sales Allowances and a credit to Accounts Receivable.
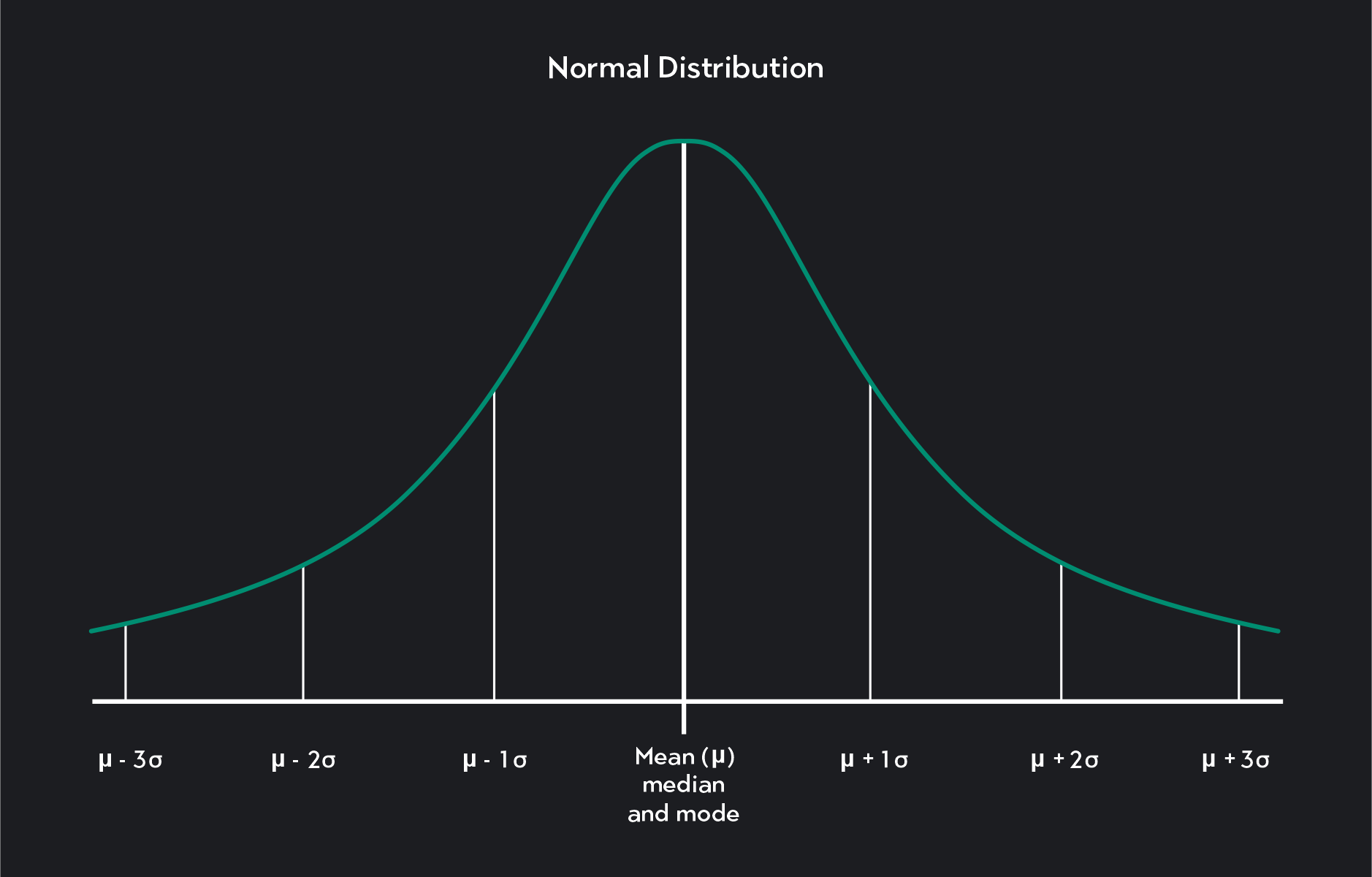
The normal distribution describes a symmetrical plot of data around its mean value, where the width of the curve is defined by the standard deviation. Similarly, many statistical theories attempt to model asset prices and assume they follow a normal distribution. In reality, price distributions tend to have fat tails and, therefore, have kurtosis greater than three. Such assets have had price movements greater than three standard deviations beyond the mean more often than expected under the assumption of a normal distribution. Even if an asset has gone through a long period where it fits a normal distribution, there is no guarantee that the past performance truly informs the future. In some settings, it’s convenient to consider a constant as having a normal distribution (with mean being the constant and variance 0, of course).
Z-scores tell you how many standard deviations away from the mean each value lies. The skewness and kurtosis of a variable are defined in terms of the standard score, so these results follows from the corresponding result for \( Z \). Many other important properties of the normal distribution are most easily obtained using the moment generating function or the characteristic function. The moments of the standard normal distribution are now easy to compute. A z-score is a measure of the number of standard deviations a particular data point is away from the mean.
A score of 93 on the test is about 1.57 standard deviations above the average test score. Heights of \(18\)-year-old males have a bell-shaped distribution with mean \(69.6\) inches and standard deviation \(1.4\) inches. The bag advertises a certain time, beyond which you risk burning the popcorn.
The basic properties of the density function and distribution function of \( X \) follow from general results for location scale families. The resulting Z-score will follow a standard normal distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. Note how the graphs become more and more symmetric as \(n\) increases. The proportion of numbers in a certain region also begins to have a fixed ratio.




 115 N 3rd St Sterling, CO 80751, USA
115 N 3rd St Sterling, CO 80751, USA